Methods of Galvanization:
Hot-Dip Galvanizing
The steel is submerged in molten zinc (~450°C).
Forms a thick, durable zinc layer with a characteristic spangled appearance.
Used for construction beams, guardrails, and outdoor structures.
Electro-Galvanizing
Zinc is applied via electroplating, creating a thinner, smoother coating.
Common in automotive parts and electronics.
Galvannealing
A combination of hot-dip galvanizing and annealing (heat treatment).
Produces a matte finish with better paint adhesion.
Used in automotive panels and appliances.
Zinc Spraying (Metallizing)
Zinc is sprayed onto steel surfaces for large or irregularly shaped items.
Advantages of Galvanized Steel:
✔ Corrosion Resistance – Zinc acts as a sacrificial anode, protecting the steel even if scratched.
✔ Durability – Can last 50+ years in harsh environments.
✔ Low Maintenance – No need for frequent painting or coating.
✔ Cost-Effective – Cheaper than stainless steel for many applications.
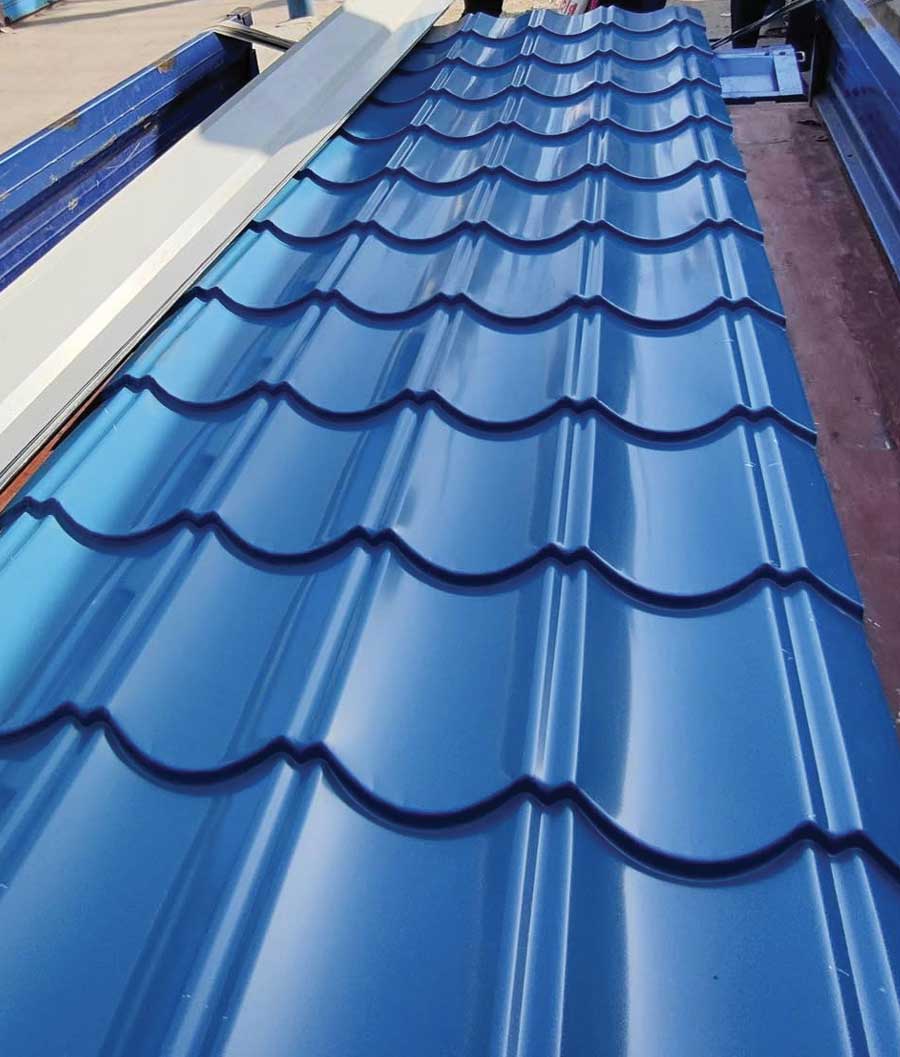
Common Applications:
- Construction: Roofing, fencing, structural beams.
- Automotive: Body panels, chassis parts.
- Household: Buckets, HVAC ducts, nails.
- Infrastructure: Guardrails, streetlights, bridges.











Please send your query of Galvanized Steel